While passive devices such as capacitors are not as attractive as microprocessors and digital signal processors, they still have reliability for automotive applications . Choosing the most reliable capacitors for today's automotive electronics requires design engineers to test a range of different component parameters and their performance characteristics. The next step is to consider the environment in which the automotive electronics are used and the specific applications they serve. Now, let's take a look at the characteristics of four dielectric capacitors - tantalum capacitors, aluminum electrolytic capacitors, multi-film capacitors and ceramic capacitors; explain the concept of temperature coefficient and voltage coefficient of capacitors; see how these and other factors are Capacitance selection that affects a particular application.
This article refers to the address: http://
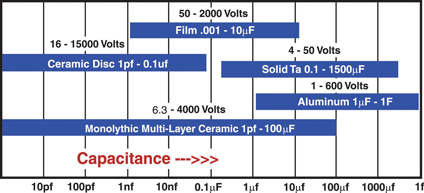
Each different capacitor dielectric has its specific capacitance and voltage range (see below). However, since the application requires a capacitance value between approximately 0.1 and 10F and a voltage less than 50V, several overlapping options may occur.
In order to find out the performance characteristics of these different types of capacitors, you need to master some basic knowledge about capacitors. We can determine the capacitance of each capacitor with a single formula:
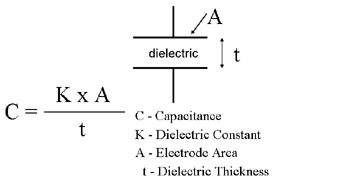
Each capacitor dielectric has a fixed dielectric constant (K), so for a given capacitive dielectric type, the size of the capacitor is proportional to the surface area (A) of the active plate of the capacitor and inversely proportional to the thickness (t) of the dielectric. . The thickness of the dielectric also determines the voltage withstand capability (rated voltage) of the capacitor.
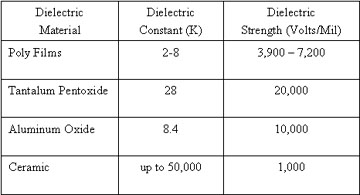
Typical dielectric constants and dielectric strength values ​​(withstand voltage) of these four basic types of capacitors are given below. As we have seen, when a low dielectric constant is coupled to a low dielectric breakdown strength (as connected to a multi-film capacitor), a low volumetric efficiency occurs. However, the size of the object is only one of the characteristics of the capacitor. For example, film capacitors are very large in size but have very efficient and stable electronic features that make up for their large size.
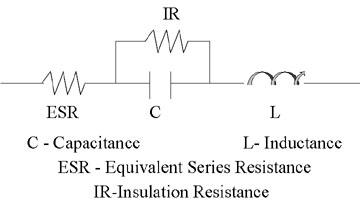
The figure below shows the working process of the capacitor. Equivalent series resistance (ESR) is the real part of the impedance and represents the loss of capacitance. The ESR value will vary with temperature, frequency, and dielectric type. The insulation resistance determines the amount of DC leakage current when a given voltage is applied across the capacitor. The leakage current varies with temperature and the magnitude of the voltage acting across the capacitor, and the leakage current of the thin film and ceramic (electrostatic) capacitors is much smaller than the leakage current of the tantalum and lead electrolytic capacitors.
Various types of capacitors are used in automotive applications, but now more and more components are used with higher capacity and complexity. Although the automotive industry uses many lead-containing components, older boards are rapidly being replaced by surface mount component (SMD) technology.
In the most common classification, capacitors are divided into two basic types of architecture: electrostatic capacitors (film capacitors and ceramic capacitors) and electrolytic capacitors (tantalum capacitors and aluminum capacitors). The electrostatic capacitance generally exhibits a very low ESR value and impedance (Z) and is a non-polar component, which means that they can be fed into the assembly line in large quantities to be inserted into the printed circuit board at high speed. In general, electrolytic capacitors provide higher capacitance, but they are polar components and must be mounted on the board with the correct polarity. The table below summarizes several basic criteria for comparing these types of capacitors.
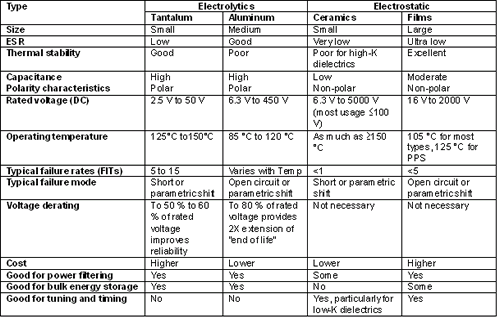
However, each type of capacitor has its own unique characteristics; even in a particular type of capacitor, whether it is suitable for a given application depends on its specific dielectric. For example, tantalum capacitors have no wear and failure mechanisms and are particularly well suited for applications that require long life and stability. For every 10C drop in temperature, the life expectancy of aluminum capacitors is doubled, but it is important to keep them away from the detergent.
Ceramic capacitors do not need to shield inrush current, but require high voltage shielding for components with high voltage ratings. Thin film and metal film capacitors are especially suitable for high current applications, and metal type capacitors have self-healing features that improve application reliability.
Due to the limited space, it is difficult to describe in detail the specific differences in electrical properties between various dielectrics. However, the following table gives a few examples to help us understand the different types of capacitors, which is necessary for us to fully evaluate the application of a given capacitor.
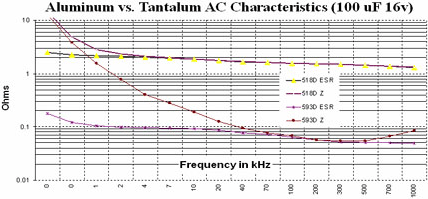
The equivalent series resistance (ESR) and impedance (Z) of tantalum capacitors and ceramic capacitors with similar capacitance values ​​are compared below.
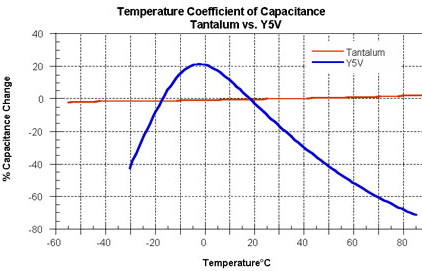
Capacitance temperature coefficient
As the temperature changes, the capacitance value also changes. This is called the temperature coefficient of capacitance (TCC). Below is a comparison of a tantalum capacitor with a Y5V ceramic capacitor.
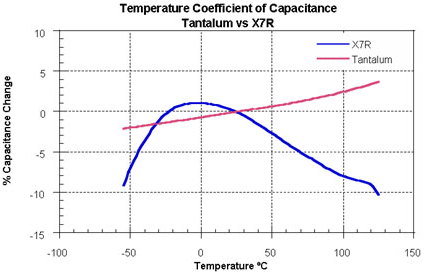
The curves below show the comparison of tantalum capacitors with X7R ceramic capacitors. In circuit design, when the entire temperature range requires a minimum capacitance, the TCC must be considered in the design.
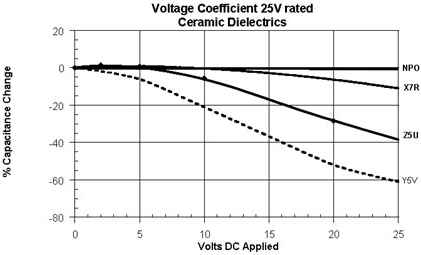
Capacitance voltage coefficient
For ceramic capacitors, the voltage applied to the capacitor also affects its capacitance (the electric field strength between the dielectrics changes the effective dielectric constant of the material). As shown in the figure above, this is not a problem when comparing rated voltages for a stable dielectric such as NPO or when the percentage of rated voltage is low. This feature is called the capacitor voltage coefficient (VCC). The capacitance voltage coefficients of several different ceramic capacitors are shown below.
in conclusion
Determining the type of dielectric that best fits a given application is not an easy task, and choosing a capacitor is a multifaceted design issue. Applications may require a minimum capacitance or a very low ESR value. The cost, size, and packaging of the capacitor must also be considered. Reliability issues at the end of life are also important. Each capacitor has its own set of features that make it the best choice for a given application.
Road Light,Double Arms Road Light,Off Road Lights,Round Road Light
Yangzhou Heli Photoelectric Co., Ltd. , https://www.heli-eee.com
