Every device on a network has both an IP address and a MAC address, which work together to ensure proper communication. A switch operates at the data link layer (Layer 2) of the OSI model, and it forwards data frames based on the MAC address found in the frame header. Each data frame consists of a header, the actual data being transmitted, and an end-of-frame marker.
Ethernet is the most widely used protocol for local area networks (LANs). It uses CSMA/CD technology to manage data transmission over various types of cables, such as coaxial, twisted pair, and fiber optic. Over time, Ethernet has evolved to support higher speeds and more reliable connections.
Repeater devices operate at the physical layer (Layer 1) and are used to extend the range of a network by amplifying and retransmitting signals. They help overcome signal degradation over long distances.
A hub, also known as a multiport repeater, connects multiple devices on the same physical medium. When one device sends a signal, the hub receives it, amplifies it, and broadcasts it to all other connected ports.
MAC Address: This is a unique physical address assigned to a network interface controller (NIC). It is used to identify devices at the data link layer of the OSI model. The MAC address is 48 bits long, with the first 24 bits assigned to manufacturers by the IEEE, and the last 24 bits assigned by the manufacturer to individual devices.
The first bit of the first byte in a MAC address determines if it's a unicast or multicast address. If all bits are set to 1, it’s a broadcast address. Layer 2 switches maintain a table of MAC addresses and their corresponding ports to efficiently forward traffic.
While the MAC address works at the data link layer, the IP address operates at the network layer (Layer 3). Their roles are distinct but complementary. IP handles routing packets between different networks, while MAC ensures that data frames are delivered to the correct device on the same network segment.
In a stable network, IP and MAC addresses are paired. When two computers communicate, they must have configured IP addresses, while the MAC address is pre-assigned during manufacturing. The ARP (Address Resolution Protocol) helps map IP addresses to MAC addresses so that devices can communicate effectively.
After hubs came switches. A Layer 2 switch uses MAC addresses to forward frames, improving network performance by sending data only to the intended recipient instead of broadcasting it to all devices.
A data frame, the protocol data unit of the data link layer, includes a header, data payload, and an end-of-frame marker. The header contains the source and destination MAC addresses, along with a type field that indicates the upper-layer protocol being used.
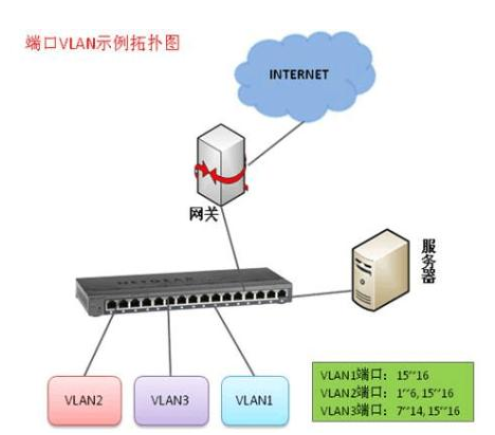
Layer 2 switches can suffer from broadcast storms, where excessive broadcast traffic causes network congestion. To prevent this, VLAN technology is used to divide the network into separate broadcast domains. VLANs isolate traffic and improve network efficiency and security.
VLANs are implemented using the IEEE 802.1Q standard, which adds a VLAN tag to Ethernet frames. This allows switches to route traffic based on VLAN ID rather than just MAC address. Communication between VLANs requires a router or a Layer 3 switch.
Port types on switches include access and trunk ports. Access ports are used to connect end devices and typically carry traffic for a single VLAN. Trunk ports, on the other hand, carry traffic for multiple VLANs and are used to connect switches together.
Access Port: Designed for connecting user devices like computers or printers. It carries traffic for a single VLAN and strips the VLAN tag before forwarding the frame.
Trunk Port: Used to connect switches or routers, allowing multiple VLANs to share the same physical connection. The VLAN tag remains on the frame as it travels across the trunk link.
To communicate between VLANs, you can use a router with sub-interfaces or a Layer 3 switch. These devices perform routing functions at high speeds, using hardware-based switching mechanisms to improve performance compared to traditional software-based routers.
modular rj45 jack,rj45 connector,rj45 jack,cat6a rj45,rj11 connector,rj11 jack,rj11 4p4c,rj11 modular jack
Dongguan Yiyou Electronic Technology Co., Ltd. , https://www.dsubminiature.com
