1. Hazard of DC system grounding
DC systems are generally used for substation control busbars, closing busbars, UPS uninterruptible power supplies, and other power and logic control loops. The DC system is an insulation system with an insulation resistance of several tens of megaohms. During normal operation, the positive and negative insulation resistances of the DC system are equal, and the ground voltage is also relatively balanced. When a little grounding occurs, the positive and negative ground voltages change, the grounding pole voltage to ground decreases, the non-grounding voltage rises, the control loop and power supply reliability are greatly reduced, but the electrical control system is generally not triggered. Faulty. However, when the DC system has two or more points grounded, it is easy to cause the logic control circuit to malfunction and the DC fuse to blow, so that the protection and automatic devices and control circuits lose power. In the complex protection circuit, the same pole is grounded at two points. Some relays may be shorted and cannot trip, causing a jump over the level, causing an accident to expand. The regulations strictly stipulate that the DC system should be grounded at the same pole and the ground should be stopped. It is also an uncertain factor based on the nature of the fault.
(1) Hazard of positive grounding of DC system
When the DC positive grounding occurs, it may cause protection and automatic device malfunction. Because the tripping coil and relay coil of the general circuit breaker are connected to the negative power supply, if another DC grounding occurs on these circuits, it may cause malfunction.
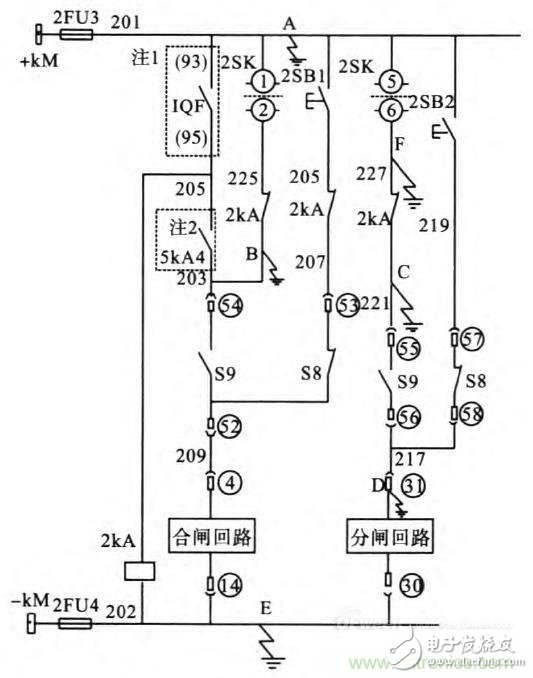
As shown in the above figure, when DC grounding occurs at two points A and B, it is equivalent to short-circuiting all external closing conditions, so that the closing coil is electrically disconnected. When two points of A and C are grounded, the external partial brake condition is short-circuited and tripped by mistake. Two points A and D, two points of A and F are grounded, which can also cause the switch to trip falsely.
(2) Harm of the grounding of the DC system negative pole
Grounding the DC negative pole may also cause protection and automatic device rejection. Because the circuit breaker's jump, closing coil, and protective relay will have a little grounding in these circuits, the coil will be shorted by the grounding point and will not operate. At the same time, the short-circuit current of the DC circuit will fuse the power supply and may burn out the relay contacts. The fuse will lose protection and operate the power.
As shown in the above figure, the DC ground fault occurs at two points C and E, D and E. When the two points of F and E are grounded, the trip coil is shorted, and the switch is rejected during protection action and operation. Similarly, the two-point grounding switch may not be able to close, such as when the two points of B and E are grounded.
The DC system ground fault is not only bad for the equipment, but also poses a threat to the safety of the entire power system. Therefore, when a DC ground fault occurs, it is necessary to find and eliminate the fault as soon as possible to avoid accident expansion and serious consequences.
2. Causes of ground fault in DC system
According to the position of the grounding point, the DC grounding can be divided into indoor and outdoor forms. According to the cause of grounding, it can be divided into the following forms:
(1) Grounding caused by rainy weather. In heavy rain, the rainwater floats into the unsealed and tight outdoor secondary junction box, causing the wiring pile head and the outer casing to conduct, causing grounding. For example, the gas relay does not have a rain cover, and the rainwater seeps into the junction box. When the water floods the terminal, DC grounding and false tripping occur. In the continuous light rain (such as rainy days), the damp air will cause damage to the outdoor cable core or the black tape, and the insulation will be greatly reduced, thus causing DC grounding.
(2) Grounding caused by damage to small animals. When the secondary junction box (box) is not well sealed, the bees will drill into the box to nest, and when the nest connects the terminal and the casing, DC grounding is induced. When the cable sheath is bitten by a mouse, it is also likely to cause DC grounding.
(3) Grounding caused by crush wear. When the secondary wire is placed against a rotating component (such as a switch cabinet door that is frequently switched), the secondary wire insulation is susceptible to wear by the rotating component, and when it is worn, it causes DC grounding.
(4) The grounding is loose and the grounding is caused. Connect to the secondary line of the terminal block of the circuit breaker mechanism box (such as the secondary line in the 10kV switch mechanism box). If the screw is not tightened, the terminal can easily slide out of the terminal when the circuit breaker is repeatedly engaged. Causes grounding on the iron piece.
(5) Misconnection causes grounding. In the secondary wiring, one end of the cable core is connected to the terminal, and the other end is mistaken as a spare core or uncharged to expose it to the iron member, causing grounding. When the cable core is removed, it is mistaken that the cable core is uncharged from the terminal block, so that no insulation wrap is made. When the opposite side of the cable core is still running, the cable core of the present side is triggered by contact with the iron piece. Ground.
(6) The component inside the plug-in is damaged and caused grounding. In order to prevent interference, the anti-interference capacitance is usually connected in parallel between the positive and negative poles and the ground in the plug-in circuit design, and the capacitor causes DC grounding when it breaks down.
3. Characteristics of DC system grounding/insulation failure
When the DC system is normal, the voltage between the positive and negative poles is generally constant. The voltage between positive and negative is 220V, the positive level is 110V to ground, and the negative level is -110V to ground. The reference potential is ground potential. It is zero potential. When DC grounding occurs, the positive and negative ground voltages will be unbalanced. For example, the positive pole is still about 110V to ground. If the negative pole is grounded, the negative pole to ground voltage amplitude will decrease, and the reference potential will also shift to the negative level. It turns out to be around -55V, and now it may become -30V, etc., and even smaller, and the voltage to the ground will increase accordingly, such as 80V. In a properly designed DC system, one pole is grounded, and the DC bus power supply voltage is constant. This is also the case when the DC system is grounded for a short period of time, but it is better to find the grounding point and eliminate it.
4. DC system grounding / insulation fault finding method
(1) Confirm the authenticity of the DC ground fault.
DC systems generally have an insulation monitoring device that alerts the unit when a DC ground fault occurs or DC insulation is reduced. When a DC ground fault occurs and the DC insulation reduces the fault alarm, the possibility of false alarm should be eliminated first. The measurement and judgment can be made according to the characteristics of the DC system ground fault.
(2) After the ground fault feature is confirmed, distinguish the polarity of the ground fault and analyze the cause of the fault.
(3) If the secondary circuit is working, or if there is equipment maintenance test, it should be stopped immediately. Pull on its working power and see if the signal is removed.
Here, the fault can be searched by first positioning the air switch to the main road, then positioning the air switch of the branch, narrowing the search range by using the network method, and dividing the DC system into several unrelated parts for searching.
If the insulation monitoring device has a fault line selection function, the fault range can be further narrowed according to the fault line prompt.
(4) For the less important DC load and the load that cannot be transferred, use the "instantaneous power failure" method to check whether the load in the circuit has a ground fault.
(5) For important DC loads, use the transfer load method to check the circuit for ground faults.
(6) To find the DC system ground fault, it should be contacted with the dispatch at any time, and cooperated by two or more people. One person operates, one person monitors and monitors the meter indication and signal changes. When selecting DC grounding by means of instantaneous power failure, the following sequence should be followed:
1 Disconnect the temporary power supply at the site;
2 break the accident lighting circuit;
3 broken contract signal power;
4 broken accessory equipment;
5 broken charging circuit;
6 breaking and closing circuit;
7 broken signal circuit;
8 break operation loop;
9 break the battery circuit.
(7) If the fault point is not detected after the above-mentioned various inspection options, the grounding of two points of the same polarity should be considered. When it is found that the grounding is behind a certain loop, the loop should be unwrapped first, and then the method of taking the fuse and removing the terminal is further adopted until the fault point is found and eliminated.
Finding DC system ground/insulation faults is a time-consuming and labor-intensive task, but according to the above search method, many detours can be taken. However, the most difficult DC grounding/insulation fault is not time-consuming and laborious, but the fault is intermittent, sometimes not, so it needs to be analyzed according to the specific situation. Generally, it is necessary to find the fault when it occurs frequently.
5. General precautions when handling DC grounding
(1) It is forbidden to use the light bulb to find;
(2) After a little grounding occurs, the principle is suspended on the secondary circuit;
(3) It shall not cause another point of DC grounding;
(4) The internal resistance of the instrument is not less than 2000 ohms;
(5) When adopting the instantaneous power-off method, it should prevent the protection from malfunctioning. For the reclosing circuit and the standby self-powered power supply, care should be taken not to switch off the power for a long time;
(6) The disassembled joints should be recorded one by one to avoid wiring errors when the joint is restored. The principle is who disassembles the joint, who recovers, and checks the recorded breakpoints one by one to avoid missing joints.
6. Measures to prevent DC system grounding/insulation failure
If a ground fault occurs in the DC system, it will have a very serious impact on the safety, stability and normal operation of the grid system. Even if the equipment is in the process of operation, the circuit breaker may be malfunctioned and the fuse or the fuse may be blown. Expand the scope of the accident. Therefore, according to the experience of Xiaobian for many years, the classification, causes and hazards of DC system grounding are analyzed, and the methods for finding and eliminating DC system ground faults are explored, and often in DC systems. Failure to be affected by natural factors such as climate, in order to better reduce the damage caused by failure, it is necessary to prevent it early. Therefore, during the daily operation and maintenance work, the pressure adopts scientific and reasonable measures to prevent the ground fault, thereby avoiding the occurrence of ground fault and ensuring the safe and stable operation of the equipment.
(1) Standardize the construction process to fundamentally avoid the occurrence of DC system ground faults and minimize safety hazards;
(2) In the process of cleaning the secondary equipment such as the outdoor terminal block and the auxiliary switch, the machine cover that is powered off can be fully utilized;
(3) It is necessary to ensure that the plugging of the secondary cable through the circuit breaker terminal box, the circuit breaker mechanism box, the isolation switch mechanism box, etc. is intact, to avoid the rain and the fog or the negligence of the staff will cause the water flow Problems such as immersion in the facility to ensure safe and stable operation of the DC system;
(4) For outdoor cables, it is necessary to strengthen the insulation test work and take corresponding measures in time to avoid the occurrence of DC system grounding accidents.
Tws Earphones,True Wireless Earphones,Good Sound Earbuds,Hifi Sound Headphones
Shenzhen Focras Technology Co.,Ltd , https://www.focras.com
