In addition to driving the rise of mobile phones, the introduction of smart phones has accelerated the innovation of communication technology. In the past few years, the increase of data transmission rate has enabled users to enjoy the new experience of high-speed mobile networks. The hot topics of 3G, 4G and 5G have always remained high. And leap to the research theme of the production and research institutes. However, the general understanding of 4G and even 5G is that mobile phones are faster and do not understand the scientific implications behind them. This article will cut through the different communication generations and guide readers to understand the principles behind these technologies. Is it electromagnetic waves? What is bandwidth? What is the difference between different generations?
Generation of mobile phones
We often hear advertisements saying: 4G LTE, where G stands for "GeneraTIon" and 4G stands for fourth generation, in order to distinguish it from previous second-generation (2G) and third-generation (3G) mobile phones. We use the European system with the highest market share in the world, which is the system currently used in Taiwan:
· Second-generation mobile phone (2G): The GSM system only supports the voice channel of line switching (Note). It mainly calls and transmits SMS through the voice channel. The GPRS system supports packet switching and therefore can access the Internet, but it uses the voice channel to transmit data. Packets, so the speed of the Internet is very slow.
· Third-generation mobile phone (3G): UMTS system supports packet switching (Note), which can access the Internet at a faster speed. Since 3G mobile phones support 2G at the same time, when we use 3G mobile phones to talk on the phone or send text messages, actually This is done using the voice channel of the GSM system.
· 4th generation mobile phone (4G): LTE / LTE-A system supports packet switching, which can access the Internet at a faster speed. Since 4G mobile phones mostly support 3G and 2G at the same time, when the mobile phone cannot find the LTE base station, The UMTS base station will be connected to the Internet, and the telephone or voice message will still be completed using the voice channel of the GSM system.
In fact, because of the high data transmission rate, the LTE system used by 4G can directly cut the voice data into packets for transmission. The principle is the same as the Skype network phone, which can make the sound quality better, but the packet switching cost is usually calculated based on the data transmission rate. It is equal to the user's long-term cost. It is a problem for telecom companies to receive more money. In contrast, circuit switching is a time-based charging, and telecom companies can make more money. Therefore, most of the telecom companies in Taiwan are currently When 4G LTE provides a phone call or a text message, it is still done using the voice channel of the GSM system.
Scientific implications of bandwidth
The general understanding of the communication generation is that the later generations show that the wider the bandwidth (bandwidth), the bandwidth is like a highway, the wider the bandwidth, the more the highway becomes more (the more lanes), the faster the speed, that is, the communication. The higher the data transmission rate; the simpler point is that the mobile phone is faster, this concept is correct, but this cognition is unscientific. To explain the bandwidth, we need to start from the electromagnetic wave.
Wireless communication transmission medium: electromagnetic wave
Electronwave (ElectromagneTIc wave) is an "energy" produced by the interaction of "Electric Field" and "Magnetic Field" which are perpendicular to each other. This energy is like a water wave when it is moving forward. It will vibrate continuously according to a certain frequency, as shown in Figure 1(a). The number of times the electromagnetic wave vibrates per second is "Frequency", and the unit is "Hertz (Hz)". Assuming that one electromagnetic wave vibrates twice in one second, the frequency is 2 Hz, as shown in Figure 1(b); After shaking for 4 times in a second, the frequency is 4Hz, as shown in Figure 1(c). For example, the communication frequency between wireless local area network (Wi-Fi) and Bluetooth is 2.4GHz, which means that it uses electromagnetic waves per second. The clock vibrates 2.4 billion times (here G means Giga, which is Billion, which stands for 1 billion, not the G of the previous 3G, 4G, 5G).
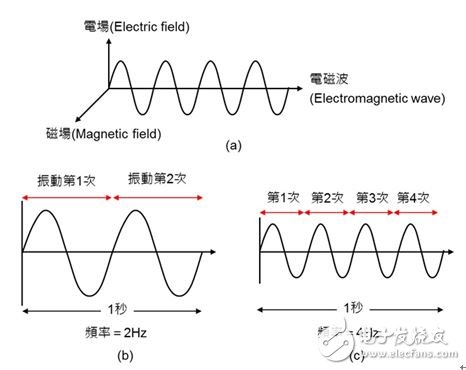
Figure 1: Definition of electromagnetic waves. (a) Electromagnetic waves are energy generated by the interaction of electric fields and magnetic fields perpendicular to each other; (b) the frequency is 2 Hz when vibrating twice per second; (c) the frequency is 4 Hz when vibrating 4 times per second.
All the electromagnetic waves naturally present in the universe are shown in Fig. 2(a). We call it "Spectrum". The middle part is light (Light), including: Infrared, IR ), visible light (light visible to the human eye), ultraviolet light (Ultraviolet, UV), so light is an electromagnetic wave; the right side is a higher frequency (higher energy) electromagnetic wave; the left side is lower frequency (lower energy) The electromagnetic wave is suitable for use as a wireless communication because it has a relatively low frequency electromagnetic wave and has good diffraction characteristics.
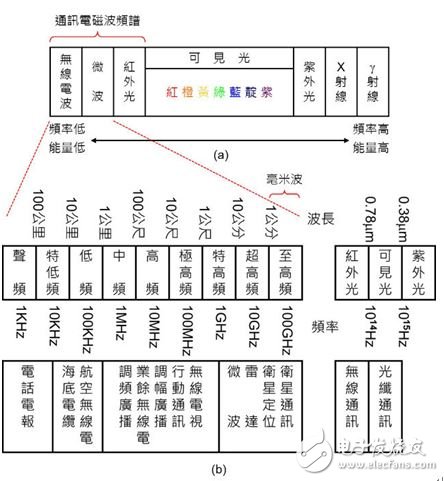
Figure 2: Electromagnetic spectrum and application. (a) electromagnetic spectrum; (b) communication electromagnetic spectrum.
The electromagnetic waves currently used for wireless communication are shown in Figure 2(b) and include:
· Electromagnetic waves with a frequency of about 100G~1GHz: usually used in satellite communication, satellite positioning, radar and microwave communication, etc., and electromagnetic waves with a frequency above 30GHz (equivalent to a wavelength below 10mm) are called "Millimeter Wave". A company plans to use it in a 5G communication system.
· Electromagnetic waves with a frequency of about 100M~1MHz: usually used in wireless TV, mobile communication (GSM / GPRS), AM (AM), amateur radio, FM radio (FM).
· Electromagnetic waves with a frequency of about 100K~1KHz: usually used in aeronautical radio, submarine cable, telephone and telegraph.
Wireless communication delivery channel: bandwidth
Bandwidth is the "frequency range" used to transmit signals. The unit and frequency are the same as Hertz (Hz), and each pair of communication users must use "different frequency range" to talk. Assume:
· A and B use electromagnetic waves with a frequency of 900~900.2MHz (bandwidth 900.2-900=0.2MHz);
·C and D use electromagnetic waves with a frequency of 900.2~900.4MHz (bandwidth 900.4-900.2=0.2MHz);
At this point we say that the voice channel bandwidth of this communication system is 0.2MHz.
The mobile phone does not know who is talking with whom, but receives a certain "frequency range (bandwidth)" electromagnetic wave signal. Therefore, when the phone calls A and B, the mobile phone receives electromagnetic waves with a frequency of 900~900.2MHz. When the mobile phone receives electromagnetic waves with a frequency of 900.2~900.4MHz, in other words, all communication components are "only recognize the frequency does not recognize people", and the electromagnetic waves of the same frequency range can only be used once, can not be reused, otherwise they will interfere with each other. .
Bandwidth and data transfer rate difference
"Bandwidth" is similar to "Data rate" and often confuses us. Here is a brief description of the differences between them:
Bandwidth is a term used in analog communication: As can be seen from Figure 1, electromagnetic waves are a continuous wave of energy. Since it is continuous, of course, it must be an analog signal. Therefore, "Bandwidth" and its unit " Hertz (Hz) refers to the physical properties of electromagnetic waves.
· Data rate is a term used in digital communication: the mobile phone first converts the voice of our speech (continuous analog signal) into discontinuous 0 and 1 digital signals, and then transmits them through the antenna. The unit of data transmission rate is "bps: bit per second", which means that several bits can be transmitted per second, that is, several 0s or 1s can be transmitted per second, for example: 1Gbps (1G = 1 billion) It can transmit 1 billion bits per second (1 billion 0 or 1).
The data transmission rate is the rate at which each bit of data is actually transmitted during digital communication. The main point is that digital signals allow us to use different modulation and multitasking techniques to make media of the same bandwidth have higher data transmission rates. New communication technologies, such as WCDMA used in 3G and OFDM used in 4G, have been invented, and will be described in detail later.
In the previous article, we learned that the spectrum of wireless communication is limited and the allocation is very strict. The electromagnetic wave of the same bandwidth can only be used once. For example, the 2G GSM900 system uses the frequency range of 890~960MHz, so other wireless communication can no longer use this frequency range. Otherwise they will interfere with each other. In order to solve the problem of plaque, engineers have developed a number of techniques to amplify spectrum usage, such as TDMA, FDAM, CDMA, OFDM, and behind these complex technologies, as long as you can master two basic concepts, you can understand the entire communication. The key to the development of technology.
These two basic concepts are ModulaTIon and Multiplex. The modulation technology is to convert the analog electromagnetic waves into different waveforms to represent two different digital signals, such as 0 and 1, so that the antenna can be transmitted to a very distant place (here only the digital modulation technology is discussed, and the early discussion is not discussed. AM, FM, this analog modulation technology). Multi-tasking technology is to distinguish electromagnetic waves from different users. Since mobile phones must be designed for use by all people, when each mobile phone throws electromagnetic waves into the air, how do you distinguish who electromagnetic waves are?
Digital modulation technology (Digital modulation)
The current mobile phone belongs to "digital communication", that is, the voice of our speech (continuous analog signal), which is first converted into discontinuous 0 and 1 digital signals by the mobile phone, and then converted into electromagnetic waves by digital modulation (analog signal) Carrying the digital signal), and finally transmitting it from the antenna, the principle is shown in Figure 3.
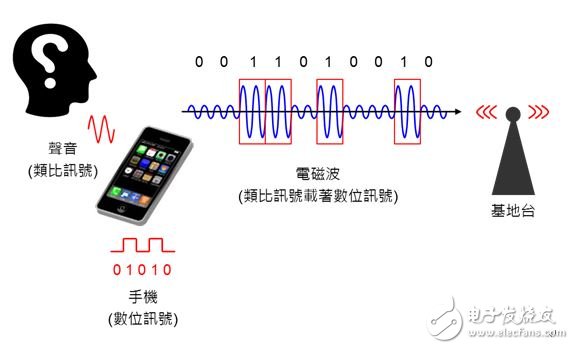
Figure 3: Schematic diagram of digital communication. (Source:the noun project)
Electromagnetic waves are continuous energy. How do we use electromagnetic waves to transmit these 0 and 1 digital signals for us? So scientists invented the following four digital modulation techniques:
1. Amplitude Shift Keying (ASK): The amplitude of the electromagnetic wave is transmitted by the digital signal (0 and 1). The small amplitude represents 0 and the amplitude represents 1, as shown in Figure 4(a).
2. Frequency shift keying (FSK): The frequency signal (0 and 1) is transmitted by the "frequency" of the electromagnetic wave. The low frequency represents 0, and the high frequency represents 1, as shown in Figure 4(b).
3. Phase shift keying (PSK): The "phase is different (waveform is different)" of the electromagnetic wave is carried by the digital signal (0 and 1). The phase 0° represents 0, the phase 180° represents 1, and Figure 4(c) Shown.
4. Quadrature Amplitude Modulation (QAM): At the same time, the "amplitude size" and "phase difference (waveform difference)" of the electromagnetic wave are transmitted along the digital signal (0 and 1). This figure is more complicated and interested. Here.
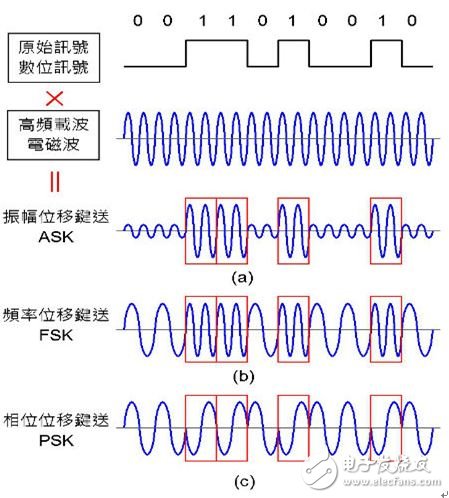
Figure 4: Digital signal modulation technology. (a) ASK: small amplitude represents 0, large amplitude represents 1; (b) FSK: low frequency represents 0, high frequency represents 1; (c) PSK: phase 0° represents 0, phase 180° represents 1.
The advantages of digital modulation technology include error detection and debugging, compression and decompression, encryption and decryption, better anti-noise capability, etc. We use 2G GSM / GPRS, 3G UMTS, 4G LTE / LTE-A, wireless local area network (Wi-Fi), Bluetooth (Bluetooth), etc. are all using digital modulation, obviously digital communication is the development trend.
The transmitting end converts the digital signal (0 and 1) into a different electromagnetic wave waveform called "Modulation". Similarly, the receiving end restores different electromagnetic waveforms into digital signals (0 and 1) called "demodulation". (Demodulation), all communication devices generally must support both transmission (modulation) and reception (demodulation). Therefore, scientists refer to the components responsible for modulation and demodulation as "modulation demodulator". The words "Modulation" and "Demodulation" are combined into a new single word "Modem". The next time you hear Modem, you know that it is a component for communication!
Multitasking technology (Multiplex)
The method of using one information channel by many people is called "Multiplex". Simply put, there is only one sky, your mobile phone will lose electromagnetic waves, and my mobile phone will also lose electromagnetic waves. Two kinds of electromagnetic waves are in the sky. Mix together, how should the receiving end distinguish between those that are yours (and you talking), those that are mine (and I talk)?
The purpose of multitasking technology is to make it available to everyone and not interfere with each other. In order to increase the data transmission rate, it may be necessary to use more than two multitasking technologies at the same time to meet the needs of everyone. Common multitasking techniques for wireless communications include the following four:
1. Time-sharing multi-tasking (TDMA): The user uses an information channel in turn according to the "chronological order". As shown in Fig. 5(a), the current 2G GSM/GPRS system uses TDMA.
2. Frequency division multi-tasking access (FDMA): The user uses an information channel at the same time according to "frequency difference". As shown in Figure 5(b), each pair of users must use "different frequency range" to talk. In fact, it is FDMA. Currently, 2G GSM/GPRS and 3G UMTS use FDMA.
3. Code division multi-tasking access (CDMA): After the data of different users is respectively calculated with a specific "Code", it is transmitted to the data channel, and the receiving end uses different passwords to distinguish the signals to be received, such as Figure 5 (c). Currently 3G UMTS uses CDMA.
4. Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiplexing (OFDM): The above-mentioned frequency division multi-tasking (FDMA) is that users transmit data simultaneously according to "frequency difference", and the principle of OFDM is similar, the only difference is that they must use "orthogonal" with each other. Frequency, this principle is more complicated and interested people can refer to here, currently 4G LTE / LTE-A, wireless local area network (IEEE802.11a / g / n), digital TV (DTV), digital audio transmission (DAB) are used OFDM.
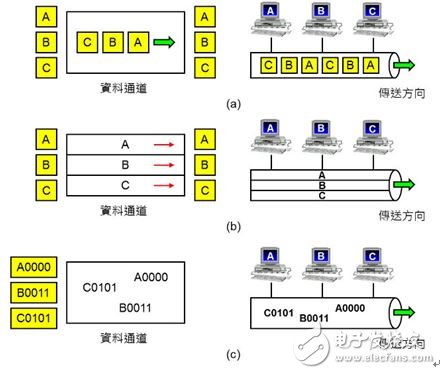
Figure 5: Multitasking technology (Multiplex). (a) TDMA: used in turn according to chronological order; (b) FDMA: used simultaneously according to frequency; (c) CDMA: computes data of different users separately from specific ciphers.
The metaphor of multitasking technology
Multi-task technology is more complicated. We can imagine that in the house, A and B should speak, and C and D should speak.
· Time-sharing multi-task access (TDMA): A and B first speak a sentence, then change the C and D, say a sentence, then change the E and talk to oneself, and so on, everyone will take turns (time-sharing) to talk to each other will not each other interference.
· Frequency division multi-task access (FDMA): A and B speak in the living room, C and D speak in the study room, and E speaks in the bedroom. Everyone in different rooms (divided) will not interfere with each other.
· Code-based multi-tasking access (CDMA): A and B speak in Chinese, C and D speak in English, and he speaks in Japanese, so that although everyone speaks in the same house, they can still distinguish each other. Language, when A and B speak in Chinese, the English of C and D and the Japanese of E and He are only disturbing the sound, and will not cause the trouble of A and B interpreting Chinese. Similarly, when C and D speak in English The Chinese of A and B and the Japanese of E and He are only disturbing the sound, and will not cause the problem of C and D interpreting English. In this case, "speaking in different languages" is like "encrypting with different passwords". .
4G and 5G technology development purposes: to increase spectrum efficiency and bandwidth
"Spectrum efficiency" is the data transmission rate (bps) of the unit bandwidth (Hz). Refer to Table 1. When the data transmission rate per unit bandwidth is high, it means high spectrum efficiency. For example, LTE can provide uploading. 2.5bps/Hz, download 5bps/Hz; LTE-A can provide upload 5bps/Hz, download 10bps/Hz, obviously LTE-A has higher spectral efficiency than LTE. Therefore, the development of 4G and 5G technologies is only for two purposes:
Increase spectral efficiency
Since the same frequency can only be used once, it is necessary to use the modified modulation and multitasking technology to increase the spectral efficiency, so that the electromagnetic waves of the same bandwidth have a higher data transmission rate, that is, put more 0 and 1 into the same The electromagnetic waves of the bandwidth are transmitted.
Increase bandwidth
Since most of the electromagnetic waves below 10 GHz in the current electromagnetic spectrum have been used, there is always a technical limit on how to improve the spectral efficiency. Therefore, scientists can only dig high-frequency electromagnetic waves that have not been used to give 5G mobile phones. Use, everyone now understands why Samsung's 5G technology wants to use "Millimeter Wave" with a frequency of 30GHz (equivalent to 10mm wavelength)! Please refer to the related news here.
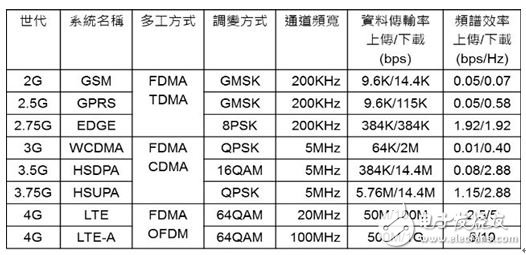
Table 1: Comparison of spectrum efficiency of digital communication systems
Note: The spectrum efficiency in Table 1 is directly divided by the data transmission rate divided by the channel bandwidth. However, different generations of communication systems use different technologies. This is not taken into account, so it is meaningful to compare the different generations in the table.
僧 粥 ,, wireless communication license and spectrum allocation
According to the previous introduction, the spectrum of wireless communication is very precious, and there are many vouchers, so the license fee is also relatively high. So who decides which frequency range the system uses will not be repeated? The domestic wireless communication spectrum is currently managed by the National Communications and Communications Commission (NCC). Every system operator (such as Chunghwa Telecom, Taiwan Big Brother, Far EasTone, etc.) must first obtain a license from NCC to operate the wireless communication service. Since the spectrum of wireless communication is very precious and the frequency range that can be used is limited, the license is limited, and the highest bidding carrier is usually licensed by public bidding. This is the fourth generation (4G) mobile broadband last year. Business release."
Not only that, because we all share the same space, if the wireless communication device arbitrarily sends out the wrong frequency signal will interfere with other communication devices, so all wireless communication devices, including the mobile phone and wireless local area network we use (Wi-Fi ), Bluetooth and other products must be tested before they can be sold.
Note: circuit switching and packet switching
Circuit switch: It means that a dedicated connection is established between the transmitting end and the receiving end to communicate. The traditional "telecom" is all circuit switching, for example: domestic and international calls, mobile Before the call, the telephone must dial first. After the switch connects the call, it can use the line exchange method. Usually, the fee is calculated according to the "use time". For example, dial the local or mobile phone, and the longer the call is used. The higher the cost.
Packet switch: It means that a line is shared between the transmitting end and the receiving end. The data to be transmitted must be cut into many smaller "packets" before communication. The current "Datacom" (Datacom) All belong to packet switching. The more data the user wants to transmit, the more packets there are. The longer the transmission time, the longer the computer network does not need to dial before communication. Just connect the network cable and use it, that is, use packet switching. The method is usually calculated by "data transmission rate". For example, Chunghwa Telecom's ADSL has different data transmission rate fees, but there is no limit to the usage time.
The electrolyte material inside the Electrolytic capacitor, which has charge storage, is divided into positive and negative polarity, similar to the battery, and cannot be connected backwards.A metal substrate having an oxide film attached to a positive electrode and a negative electrode connected to an electrolyte (solid and non-solid) through a metal plate.
Nonpolar (dual polarity) Electrolytic Capacitor adopts double oxide film structure, similar to the two polar electrolytic capacitor after two connected to the cathode, the two electrodes of two metal plates respectively (both with oxide film), two groups of oxide film as the electrolyte in the middle.Polar electrolytic capacitors usually play the role of power filter, decoupling (like u), signal coupling, time constant setting and dc isolation in power circuit, medium frequency and low frequency circuit.Non-polar electrolytic capacitors are usually used in audio frequency divider circuit, television S correction circuit and starting circuit of single-phase motor.
Electrolytic capacitor
Electrolytic Capacitor,Aluminum Electrolytic Capacitor,High Voltage Electrolytic Capacitor,12V Electronic Components Capacitor
YANGZHOU POSITIONING TECH CO., LTD , https://www.yzpstcc.com
