With the increasing demand for cable bandwidth for current video and data transmission services, the downstream data rate is increasing year by year at a rate of 30% to 40%. In addition, consumers also want to use the increasing number of connected devices in their homes at the same data rate. From a long-term perspective, it is difficult for the current analog downlink modems to meet the cost requirements. Service providers have also noticed that it is very expensive to upgrade the existing access platform to meet the increasing bandwidth requirements.
This shows that users and service providers are facing the same problem: analog transceivers have been unable to meet the increasing bandwidth requirements. Replaced by a new generation of digital RF modulators, it can provide high-density, low-cost solutions to meet future bandwidth requirements. The digital RF modulator uses a direct frequency conversion architecture, enabling the Converged Access Platform (CCAP) to support quadrature amplitude modulation (QAM) transmission across the entire frequency band. The capacity of these digital RF modulators can be up to 32 times that of analog modulators, and the power consumption of each QAM transmit channel is only about one-twentieth of that of analog technology.
This article introduces the principles and advantages of using a direct conversion architecture to implement a digital QAM modulator in a CCAP system.
Reasons for replacing analog transceivers with direct conversion transceivers
The CCAP platform of CATV (Figure 1) integrates two downlink service transmission methods: one is the edge QAM device for video, and the other is the cable modem terminal system (CMTS) for high-speed Internet access . QAM modulated digital carriers include broadcast TV and narrowcast services, such as video on demand (VoD), switched digital video (SDV), and high-speed Internet. These carriers range from 50MHz to 1000MHz bandwidth downstream CATV spectrum. Up to 158 (6MHz bandwidth) QAM carriers (channels) occupy the entire spectrum of each RF port at the front end of the CCAP. Each line card can hold up to 8 ~ 12 RF ports, and each 13RU CCAP chassis can hold 5 downstream line cards.
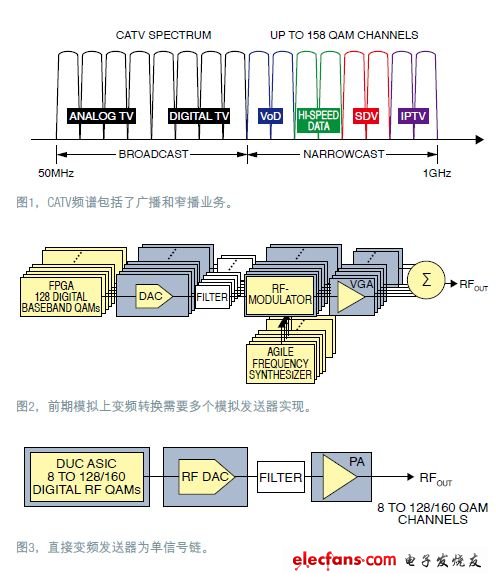
The downstream CCAP physical layer (PHY) requires highly dense RF modulators, so these QAM modulators must have low power consumption, scalability, and QAM carrier frequency agility. The previous RF front-end equipment combined QAM carriers from multiple superheterodyne analog transmitters to make it located in the CATV spectrum (Figure 2). In this scheme, the power of each CCAP RF port may require more than 300W. Direct conversion transmission It is easy to realize the up-conversion (DUC) and modulation of QAM carrier in the digital domain, and can be realized by ASIC or FPGA (Figure 3). Because the entire spectrum of the QAM carrier is transmitted through a single RF link, this digital architecture can only be achieved through a wideband RF digital-to-analog converter (RF DAC).
The direct conversion transmitter has obvious advantages in the CCAP system: the entire signal processing is realized in the digital domain, benefiting from the CMOS process structure. The CMOS process allows a very high channel density with a small footprint and low power consumption. The advantages of this method will be easily understood through the following example.
The MAX5880 is a 128-channel DUC and QAM modulator that drives an RF DAC. It receives forward error correction (FEC) encoded symbols from the FPGA, performs QAM modulation, pulse shaping, and resampling for each QAM channel. The QAM channel is combined, interpolated, and modulated to drive the RF DAC. The sampling rate of the RF DAC must be higher than 2Gsps for synthesizing the entire CATV band signal. It must also meet strict DOCSIS RF specifications. This design uses a 14-bit 4.6Gsps MAX5882 RF DAC.
Pull the trigger by one hand and the grip will be opened easily and release instantly to quickly insert or remove wire.
Special designed for gripping a wider range of cables.
Forged alloy steel construction is durable yet lightweight, yellow chromate finish protects grips from rust and corrosion.
Widely to be used in the power, communications, and general construction fields to pull wire and cable.
Used for pulling up lines to tension only. Not to be used as anchors.
Jaw is available for large teeth, aggressive teeth, and fine teeth for different applications.
Warnings: Do not exceed rated capacity and always match proper size and type of grip to application. Before each use, make sure to clean jaw area and inspect grip for proper operation to avoid slippage.
Cable Gripper,Come Along Clamp,Wire Rope Grip,Self Gripping Clamp,Ngk Cable Gripper,Ngk Cable Puller
NINGBO BEILUN TIAOYUE MACHINE CO., LTD. , https://www.spool-manufacturer.com
