In 2017, collaborative robots, or cobots, started to drive the growth of the robotics market. According to BIS Research, by 2021, the market for collaborative robots was expected to reach 150,000 units, with sales projected to hit $2 billion. Many industries are now adopting cobots as a way to move toward a more automated future. These robots are not only efficient but also safe and easy to integrate into existing workflows.
What makes collaborative robots stand out is their ability to perform tasks that were previously done manually across various work areas. Thanks to built-in safety features like force feedback and collision detection, they can safely work alongside humans without the need for extensive protective barriers. Universal Robots is one of the leading companies in this field. Their recent white paper outlines the seven most common applications of collaborative robots, highlighting their versatility and value in modern manufacturing.
**Pick and Place**
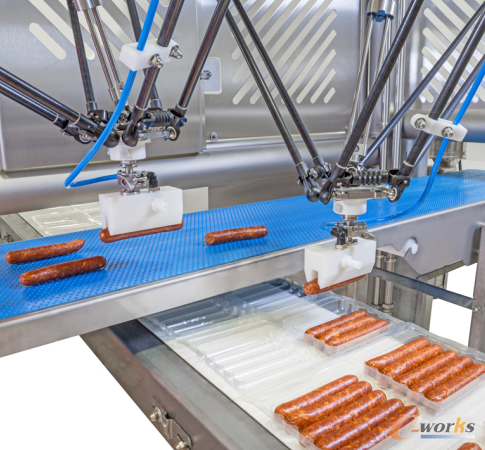

*Figure: A typical pick and place robot. The robot recognizes parts and objects and wraps them.*
Picking and placing is one of the most repetitive tasks in many industries. Manual handling can lead to errors, especially in dirty environments, and repeated movements can cause physical strain on workers. By using collaborative robots for these tasks, companies can reduce the burden on human workers while increasing efficiency. This task involves picking up an object from one location and placing it in another, often used in packaging, sorting, or loading products from conveyors. Advanced vision systems are typically required to detect and handle items on moving belts. The robot uses an end effector, such as a gripper or vacuum chuck, to grasp and move the object.
**Equipment Care**
Equipment care involves monitoring machines like CNC tools or injection molding machines. Workers often have to stay close to these machines for long periods, changing tools or restocking materials. This process is not only time-consuming but also monotonous. Collaborative robots can take over these tasks, allowing employees to focus on more complex activities. These robots are equipped with I/O hardware that communicates with the machines, signaling when to start a new cycle or when materials need to be replenished. This improves productivity and reduces downtime.
**Packing and Palletizing**
Packing and palletizing fall under the broader category of pick and place. Before products are shipped, they must be properly packaged, assembled, and placed on pallets. This work is highly repetitive and often involves small loads, making it ideal for automation with collaborative robots. In mass production settings where product variety changes frequently, quick changeover is essential. Conveyor tracking technology helps synchronize the robot’s movements with the conveyor belt. For irregularly shaped items, a vision system is also used to guide the robot accurately.
**Processing Operations**
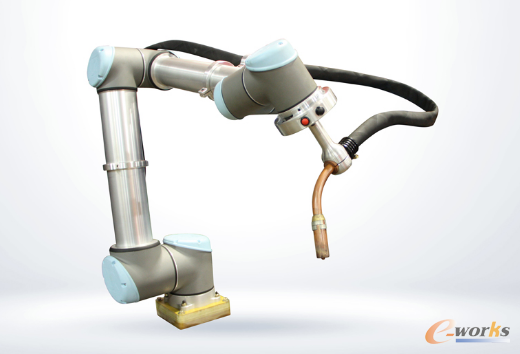
*Figure: The Universal Robot is one of the few manufacturers that can provide specialized soldering end effectors. Other collaborative robots also have different end effectors for different processing tasks, such as various glue dispensers.*
Collaborative robots are widely used in processing operations such as welding, gluing, and soldering. These tasks require precision and consistency, which robots can deliver reliably. End effectors vary depending on the task—some are designed for gripping, while others are used for applying adhesives or performing delicate soldering. This flexibility allows cobots to adapt to a wide range of industrial needs, making them a valuable asset in modern manufacturing.
Tungsten Heavy Alloys,Gold Tungsten Alloys,Heavy Metal Alloys,Magnesium Tungsten Alloy
Shaanxi Xinlong Metal Electro-mechanical Co., Ltd. , https://www.cnxlalloys.com
