1. Primary Circuit - The main electrical wiring system that starts from the generator, passes through transformers, and extends to transmission and distribution lines and electrical equipment is known as the primary circuit.
2. Secondary Equipment - These are auxiliary devices used for monitoring, measuring, controlling, and protecting the primary equipment. Examples include instruments, relays, control cables, and signaling devices.
3. Secondary Circuit - A circuit formed by connecting secondary equipment in a specific sequence is referred to as a secondary circuit or secondary system.

4. Low-Voltage Switch - A switching device used to open or close AC or DC circuits below 1000 volts. It differs from the low voltage defined in safety regulations (voltage to ground less than 250 volts).
5. Contactor - A low-voltage switch designed to control load current at a distance. It is commonly used in motor circuits that require frequent starting and control.
6. Automatic Air Switch - Also known as an automatic switch, it is the most complete type of low-voltage switch. It can cut off both load current and short-circuit current, making it ideal for high-power low-voltage circuits.
7. De-excitation Switch - A single-pole automatic air switch specifically used for the excitation circuit of a generator.
8. Isolation Switch - A switch with a visible break and no arc-extinguishing mechanism. It can be used to open or close unloaded lines, voltage transformers, and small-capacity unloaded transformers. Its main purpose is to isolate the power supply when equipment is under maintenance.
9. High-Voltage Circuit Breaker - Also called a high-voltage switch. It can open or close no-load and load currents in high-voltage circuits and also interrupt short-circuit currents through relay protection during faults. It has a complete arc-quenching structure and strong current interruption capability.

10. Arc Suppression Coil - A variable inductor with a core installed at the neutral point of a transformer or generator to reduce ground fault current and suppress arcs during single-phase grounding faults.
11. Reactor - An inductive coil with low resistance, insulated from itself and the ground. It is connected in series to limit short-circuit current in the circuit.
12. Eddy Current Phenomenon - When a coil is placed on a solid core, the changing magnetic flux induces currents in the core, forming eddy currents that resemble vortices within the material.
13. Eddy Current Loss - Energy lost due to the heating effect of eddy currents in the core, which reduces efficiency and increases temperature.
14. Small Current Grounding System - A system where the neutral point is either ungrounded or grounded through an arc suppression coil.
15. High Current Grounding System - A system where the neutral point is directly grounded.

16. Armature Reaction - The effect of armature current on the main magnetic field in a machine, causing changes in the magnetic flux distribution.
17. Asynchronous Motor - Also known as an induction motor, it operates based on electromagnetic induction. The rotor speed is always slightly less than the rotating magnetic field's speed, hence the term "asynchronous."
18. Synchronous Speed - The rotational speed of the magnetic field produced in the air gap of an asynchronous motor, determined by the number of poles and the frequency of the supply current.
19. Slip Rate - The ratio of the difference between synchronous speed and actual motor speed to the synchronous speed, expressed as a percentage.
20. Star-Delta Starting - A method where the stator windings are initially connected in a star configuration during starting and then switched to a delta configuration after the motor reaches operating speed.
21. Absorption Ratio - The ratio of insulation resistance measured at 60 seconds to that measured at 15 seconds after applying a DC voltage to the insulating material.
22. Working Grounding - A grounding connection made at a specific point in the power system to ensure safe operation and prevent dangerous voltages caused by equipment failure.

23. Protective Earthing - Connecting the metal casing of electrical equipment to the earth to prevent electric shock in case of insulation failure.
24. Protection and Zero Connection - Connecting the metal casing of equipment to the neutral line in a grounded power system to enhance personal safety.
25. Isolation Switch - A switch with a visible break and no arc-extinguishing mechanism, used to isolate power when equipment is under maintenance.
26. High-Voltage Circuit Breaker - A critical component in high-voltage systems that can disconnect or connect no-load and load currents, and also interrupt short-circuit currents using protective relays.
27. Arc Suppression Coil - Installed at the neutral point of a transformer or generator to reduce ground fault current and suppress arcs during single-phase faults.
28. Reactor - An inductive coil used to limit short-circuit current in a circuit by introducing impedance.

29. Eddy Current Loss - The energy loss caused by the heat generated from eddy currents in a core, reducing the efficiency of electrical devices.
30. Small Current Grounding System - A system where the neutral point is not grounded or grounded via an arc suppression coil to minimize fault current.
31. High Current Grounding System - A system where the neutral point is directly grounded to provide a stable reference for the electrical network.
32. Armature Reaction - The influence of the armature current on the main magnetic field, altering its distribution and affecting the performance of the machine.
33. Arc - A continuous flow of ionized particles formed by multiple sparks, often seen in electrical discharges.
34. Phase Sequence - The order in which the phases of a three-phase AC system reach their peak values. It determines the direction of rotation in motors and the behavior of unbalanced systems.
35. Relay Pickup Current - The minimum current required to activate a relay and initiate its operation.

36. Current Relay - A relay that operates based on the magnitude of the current flowing through its coil.
37. Voltage Relay - A relay that activates based on the voltage applied to its coil.
38. Fast Relay - A relay that operates in less than 10 milliseconds, providing rapid response in critical applications.
39. Instantaneous Protection - A protection mechanism that acts immediately when the current reaches a set threshold, without any time delay.
40. Differential Protection - A protection technique that detects internal faults by comparing the currents entering and leaving a protected zone.
41. Zero-Sequence Protection - A protection method that responds to zero-sequence currents and voltages, typically used in ground fault detection in power systems.
42. Distance Protection - A protective device that measures the impedance between the fault location and the protection installation to determine the fault distance.
43. Automatic Reclosing - A system that automatically re-closes a circuit breaker after a fault has been cleared, improving system reliability and reducing downtime.
44. Comprehensive Reclosing - A type of reclosing that handles different types of faults by selectively tripping and reclosing phases based on the fault condition.
45. Acceleration After Reclosing - A feature that allows the protection system to act faster after a reclosing attempt, especially in cases of permanent faults.
46. Protection - A system that ensures the safe and stable operation of electrical equipment by selectively removing faulty components from the system.
47. Backup Protection - A secondary protection system that activates if the main protection fails or the circuit breaker refuses to operate.
48. Power Factor - The ratio of real power (P) to apparent power (S), indicating the efficiency of power usage in an AC circuit.
49. Switching Operation - A series of actions performed to change the state of an electrical device or modify the system’s operating mode. Common operations include transformer energization, line de-energization, generator startup, busbar switching, and grounding wire installation/removal.
50. No-Load Loss - The power consumed by a transformer when one winding is energized while the others are open, representing core losses due to hysteresis and eddy currents.
51. No-Load Current - The current drawn by a transformer when it is running without load, primarily used to establish the magnetic flux in the core.
52. Short-Circuit Loss - The power dissipated in the windings of a transformer when one winding is shorted and the other is supplied with rated current, representing copper losses.

53. Short-Circuit Voltage - The voltage required to produce the rated current in one winding of a transformer when the other is shorted, expressed as a percentage of the rated voltage. It reflects the transformer’s impedance characteristics.
10KW-200KW Three-Phase Inverter
10KW-200KW Three-Phase Inverter
CHARACTERISTIC
â—Online working mode design, high speed static switching..Superior load characteristics
â—Perfect protection function
â—High performance dynamic characteristicselntelligent battery management
â—Optional battery patrol module
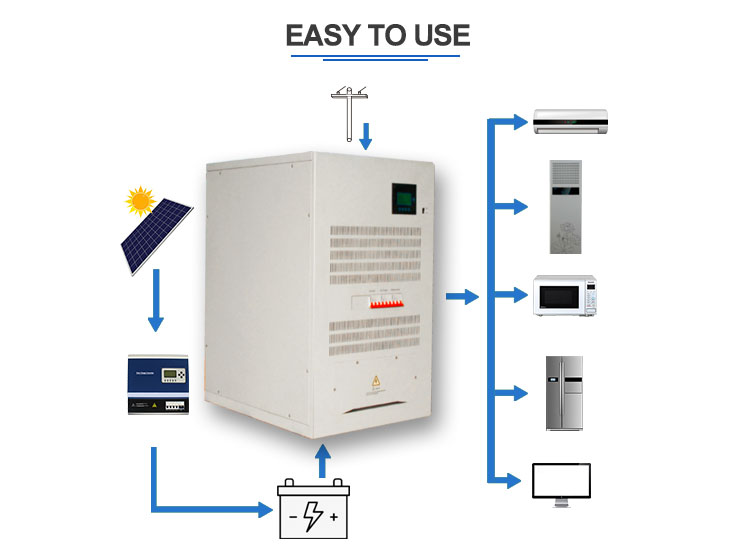

Nkm Hybrid Inverter With Mppt Charge,Inverter Power Inverter,Hybrid Inverter Charger,Hybrid Grid Tie Inverter
suzhou whaylan new energy technology co., ltd , https://www.xinlingvideo.com
