100G line solution
In the field of 100G line transmission technology, the mainstream solution in the industry is to adopt PDM-QPSK coding and modulation technology, which uses coherent reception at the receiving end and compensates for dispersion and PMD through digital changes and DSP processing. The mechanism of each manufacturer on the modulation side is basically the same. Both of them use polarization modular division multiplexing and four-phase modulation to reduce the high-speed 100G signal transmission code rate. Through processing, the code rate is reduced to 28Gbps. AD conversion, DSP algorithm processing and FEC encoding and decoding at the receiving end are reflected in the OSNR tolerance, CD / PMD compensation value and specific transmission specifications. The transmission specifications of PDM-QPSK on the line can reach 1200km (15 * 22dB), line wavelength The frequency interval is 50GHz, and the transmission capacity can reach 8T. PDM-QPSK modulation and Coherent detection technology have been determined by OIF International Standardization Organization as the standard transmission and reception method for 100Gbps long-distance transmission in the future, which has become a hot research topic in the industry.
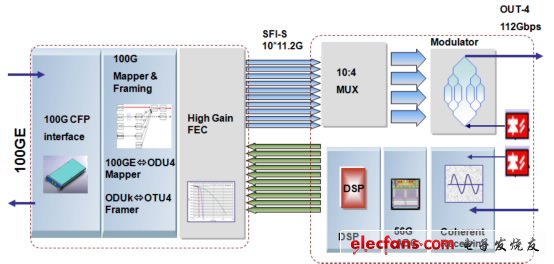
Other 100G line coding solutions in the industry also include the 2SC-DP-QPSK scheme, which is basically the same as the PDM-QPSK acceptance mechanism. It also uses coherent reception technology. 100G uses two 56G sub-wavelengths through inverse multiplexing to achieve a frequency interval of 25GHz The line transmission rate can also reach 8T, which is the same as the spectral efficiency of PDM-QPSK. Due to the use of 56G four-phase modulation and polarization multiplexing, its code rate is only 14Gbps, which results in a rate close to 10G. When mixed with 10G, the XPM effect is larger and the ability to resist nonlinearity is relatively weak. In addition, due to the use of 2 With the transmitter, the device implementation is more complicated, and the cost is higher.
Another 100G solution is OPFDM-DQPSK. The receiving end uses non-coherent receiving technology, which is mainly used for compatible mixed transmission with the existing network's 10G / 40G non-coherent system. Two 56G wavelengths are used in reverse multiplexing on the line The advantage is that the system design is very similar to the optical layer parameters of the original non-coherent 10G / 40G system, and does not bring additional dispersion costs. The line frequency interval is also 50GHz, and the system capacity can reach 4T. Metropolitan area network application.
100G network solution
Network mixed transmission solution
As the 100G era is coming, how 100G and existing networks are compatible for transmission has become the focus of the industry's attention. Several major influencing factors need to be considered and evaluated, including the system's OSNR tolerance, CD / PMD tolerance, and nonlinear effects. There are mainly three types of mixed transmission scenarios:
First, coherent 100G (PDM-QPSK) and non-coherent 10G / 40G existing system mixed transmission. As we all know, a 100G solution with a coherent receiving end can bring many benefits to the network, such as saving DCM modules, simpler optical layer planning, etc. However, with the original system, especially 10G non-coherent mixed transmission, the original system DCM module How much impact the coherent system will bring has always been a concern. Laboratory tests have shown that the cost of additional OSNR of non-coherent systems to coherent systems is not higher than 0.5dB, and the impact is small, and the input optical power of coherent 100G can reach 1 ~ 2dBm, which is close to the existing 10G system, only If OSNR parameters can meet the design requirements of 100G and 10G at the same time, compatible mixed transmission can be achieved.
Second, the mixed transmission of coherent 100G and coherent 40G systems. For the 40G coherent system, there are currently two mainstream coding technologies in the industry, one adopts 2-phase modulation PDM-BPSK, the code rate is 21.5Gbps, and the fiber input power is close to that of 100G coherent and 10G systems. ; The other 40G coherent uses 4-phase modulation PDM-QPSK, the code rate is 11.25Gbps, the non-linearity is weak, the fiber input power is low, and the 100G coherent compatible mixed transmission is expensive, so it needs to be carefully designed in the mixed transmission scenario .
Third, incoherent 100G (OPFDM) and incoherent 10G / 40G mixed transmission. The design parameters of the non-coherent 100G optical layer are close to the existing 10G / 40G system, and the impact cost is relatively small. As long as the OSNR satisfies the design, the mixed transmission can be achieved.
High frequency board dielectric material has the following characteristics
1. It has the characteristics of small signal transmission loss, short transmission delay time and small signal transmission distortion.
2, has excellent dielectric properties (mainly DK, DF). Moreover, this dielectric property (DK, DF) maintains its stability under environmental changes in frequency, humidity, and temperature.
3. High-precision control with characteristic impedance (Zo).
4, has excellent heat resistance (Tg), processability and adaptability.
Rf Module Pcb,Tin High Frequency Circuit Board ,Rigid Flexible High Frequency Pcb,High Frequency Circuit Board
Chuangying Electronics Co.,Ltd , https://www.cwpcb.com
