
The Evolution of Global Intelligent Manufacturing
Intelligent manufacturing has evolved alongside the rapid advancement of information technology. In 1988, Professor P.K. Wright from New York University and D.A. Bourne from Carnegie Mellon University introduced the concept of "Smart Manufacturing" in their book, marking the first formal proposal of intelligent manufacturing. They emphasized that the goal was to replicate the expertise of skilled workers through knowledge engineering, advanced software systems, robot vision, and machine control, enabling the production of small batches of products without manual intervention.
By the 1990s, with the rise of artificial intelligence and information technology, intelligent manufacturing began gaining traction globally. Developed nations such as the United States and Japan invested heavily in research, establishing dedicated projects and experimental facilities. This period saw significant progress in both theoretical development and practical implementation of smart manufacturing technologies.
In the 21st century, especially after the 2008 financial crisis, many developed countries re-evaluated their industrial strategies. The idea of “re-industrialization†emerged, aiming to strengthen domestic manufacturing. At the same time, breakthroughs in big data, cloud computing, and other digital technologies accelerated the shift toward intelligent manufacturing. Countries began to prioritize smart manufacturing as a core direction for future growth, offering substantial policy support to gain a competitive edge in the global tech race.
Figure 1: The History of Intelligent Manufacturing

Current State of Global Intelligent Manufacturing
The intelligent manufacturing industry encompasses a wide range of sectors, including smart equipment (such as robots, CNC machines, service robots, and automation tools), the industrial internet (machine vision, sensors, RFID, and industrial Ethernet), industrial software (like ERP, MES, and DCS), and the integration of 3D printing and automated production lines.
Globally, the U.S., Germany, and Japan lead in smart manufacturing, but many other countries are also actively investing. For example, the EU has prioritized advanced manufacturing as a strategic focus. In 2010, it launched the FP7 Cloud Manufacturing Framework, and in 2014, initiated the Horizon 2020 program, emphasizing intelligent manufacturing as a key innovation area. Canada also focused on smart systems, including robotics, human-machine interfaces, and dynamic system integration in its 1994–1998 strategy plan.
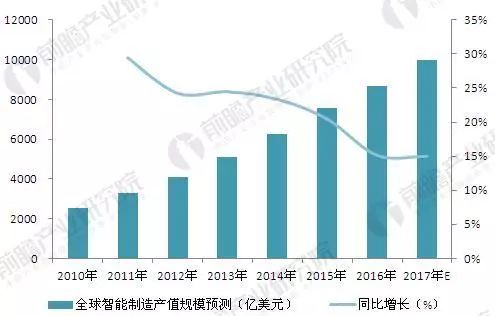
According to China’s Ministry of Industry and Information Technology, China’s manufacturing output accounted for 19% to 21% of the world total since 2010. In 2016, China's intelligent manufacturing sector reached 1.2333 trillion yuan. Based on this, global intelligent manufacturing output was estimated at around $868.7 billion in 2016. By 2017, the industry continued to grow rapidly, reaching an estimated $1 trillion annually.
Figure 2: Global Smart Manufacturing Output Value from 2010 to 2017 (Unit: Billion USD, %)
Current State of Global Intelligent Manufacturing Equipment
â—† Status of the Global Industrial Robot Industry
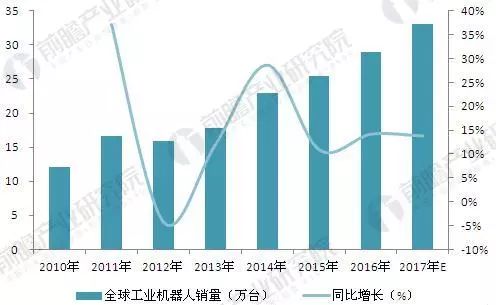
Industrial robots are a cornerstone of intelligent manufacturing. According to the International Federation of Robotics (IFR), global sales of industrial robots grew significantly in 2016, reaching approximately 290,000 units—a 14% year-on-year increase. China alone sold 90,000 units, a 31% increase compared to the previous year. IFR forecasts that global industrial robot sales will maintain an average annual growth rate of around 12% over the next decade, reaching about 330,000 units in 2017.
Figure 3: Changes and Forecasts in Global Industrial Robot Sales (2010–2017) (Unit: 10,000 Units, %)
Source: IFR (International Robotics Federation) & Prospective Industry Research Institute
â—† Status of Global CNC Machine Tools
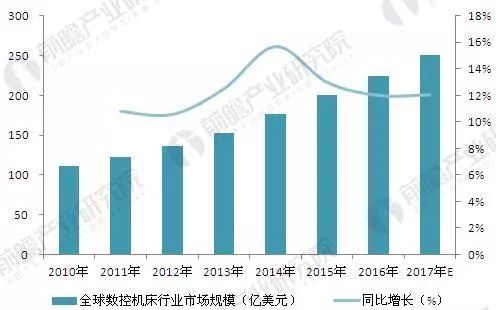
CNC machine tools play a vital role in modern manufacturing. Over recent years, they have become more advanced and intelligent, supporting the growth of smart manufacturing. In 2016, the global market for CNC systems reached $22.4 billion, making up 63.9% of the total machine tool electronics market. It is projected to reach $25.1 billion by 2017.
Figure 4: Market Size Trends of the Global CNC Machine Tool Industry (2010–2017) (Unit: Billion USD, %)
Future Prospects and Trends in Global Intelligent Manufacturing
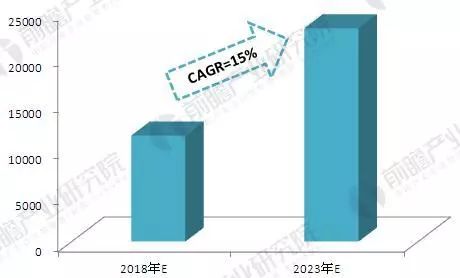
In 2017, connected and sensory robots continued to drive the development of intelligent manufacturing. As AI technology advances, industrial robots are becoming more autonomous, capable of perceiving, learning, and making decisions independently. According to forward-looking industry research, the global smart manufacturing sector is expected to grow at an average annual compound rate of 15% in the coming years. By 2023, the global output value of intelligent manufacturing is estimated to reach around $230.8 billion.
Figure 5: Forecast of Global Intelligent Manufacturing Output Value (2018–2023) (Unit: Billion USD, %)
Beam Splitter,Dichroic Beam Splitter,Optical Beam Splitter Cube,Beam Splitter Cube
Danyang Horse Optical Co., Ltd , https://www.dyhorseoptical.com